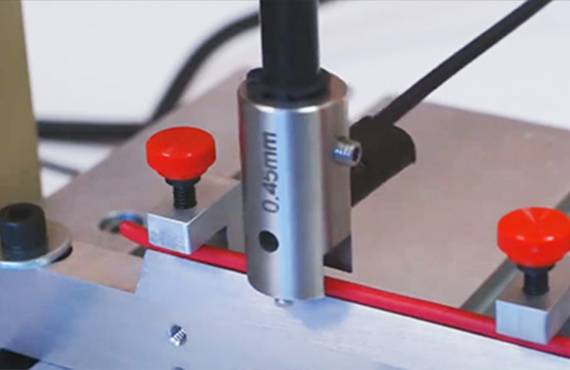
Cable abrasion testing typically involves the following major steps:
Sample Preparation: A representative sample is cut from the cable, usually a small piece of sample that includes the outer sheath or insulation.
Abrasion device: Using a specialised abrasion device or equipment, the sample is brought into contact with a friction or abrasion surface to simulate the wear and tear that the cable is likely to encounter in actual use.
Friction and pressure: Parameters of friction and pressure can be adjusted during the test to simulate wear under different conditions.
Test Cycle: Samples are typically tested during a set test cycle, the length and conditions of which can be determined according to specific test criteria or requirements.
Evaluation: At the end of the test, the degree of wear of the sample is assessed, usually by measuring weight loss, morphology of the worn surface and other relevant properties.
The results of cable abrasion testing can be used to assess the quality and durability of cable materials. This helps manufacturers to ensure that the cables they produce are able to withstand mechanical wear and friction in real-world applications in order to extend their service life and maintain performance. In addition, abrasion testing helps to ensure the reliability of cables in specific environments, such as in industrial premises, construction sites or other places where there may be a potential risk of abrasion.